A Day of Learning Health Systems

The AAMC, in collaboration with the Donaghue Foundation, recently hosted a “Building Learning Health Systems at the Point of Care” roundtable, which serves as the culminating activity for the AAMC’s Donaghue-funded opportunity award. The purpose of this research was to enhance developments of Learning Health Systems by 1) evaluating the Donaghue Greater Value Portfolio grant program awardees and identification of implementation-facilitating attributes of their health systems and 2) hosting a convening at the AAMC to share models of learning health system design, showcase examples of implementing research to drive system change, and developing a call to action to replicate lessons learned through the AAMC/Donaghue partnership. This roundtable brought together researchers, policymakers, funders, and health system leaders to discuss strategies for broadening the impact of learning health systems design. This meeting aimed to gain insight into relevant learning health system challenges, changes, and opportunities for advancement from thought leaders by discussing the critical attributes of learning health systems and ways to advance the feasibility and sustainability of research, data generation, and analysis to drive continuous improvement in both within and across institutions.
A learning health system (LHS) is a process or framework used by institutions and organizations to facilitate continuous learning and implementing new knowledge related to the healthcare enterprise. LHSs are significant in facilitating sustainable partnerships between researchers, teaching hospitals, and community health sites to use evidence to improve quality, safety, equity, and system effectiveness and to enhance the education of clinicians, patients, and community members. The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) defines the general framework of an LHS as a cyclic cycle that simultaneously integrates research and data to create new evidence, which is then used in practice.
Figure 1: About Learning Health Systems Content last reviewed May 2019. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD.
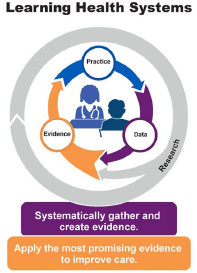
Throughout the roundtable, attendees shared ways to engage with LHSs professionally. This discussion further solidified the following characteristics of effective LHSs:
- Leadership and a strategic plan that encourages patient and clinician engagement in translational and implementation research.
- A clinical environment that values engagement in research, e.g., institutional support of academic staff time.
- A data system that facilitates electronic health record (EHR) analysis and the creation of research data sets.
- A translational research center or other structure that facilitates clinical and research staff interactions supports training, provides research tools, and includes mechanisms to support staff time in research.
- Resources focused on the engagement of patients and the community in research.
After the roundtable, all attendees were asked to reflect on and respond to each of the posed critical questions related to their unique roles, capacities, and institutional practices and initiatives.
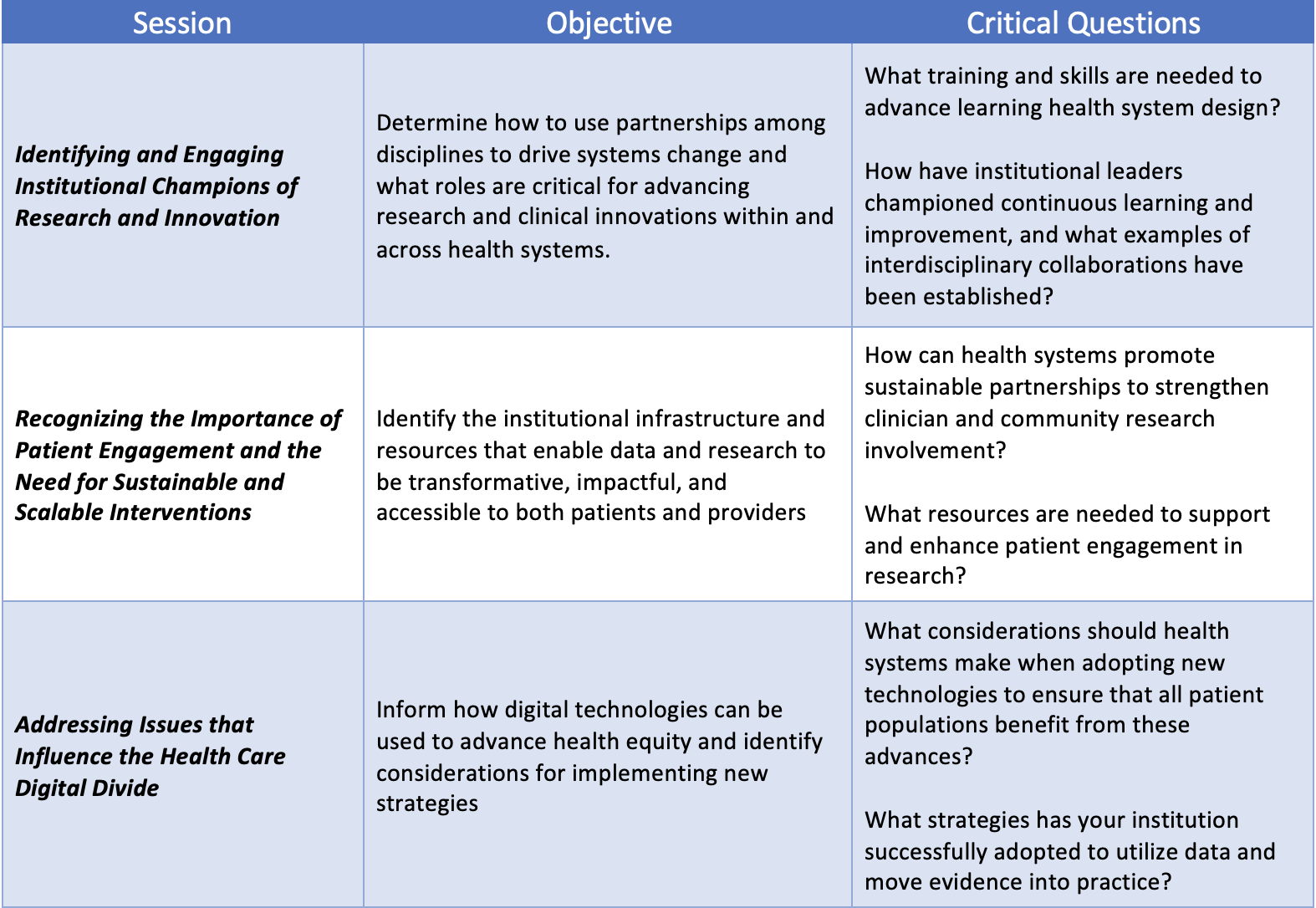
Post-Roundtable Key Points
Understanding, developing, and implementing sustainable learning health systems requires commitment and a culture that fosters continuous learning, evaluation, and improvement.
